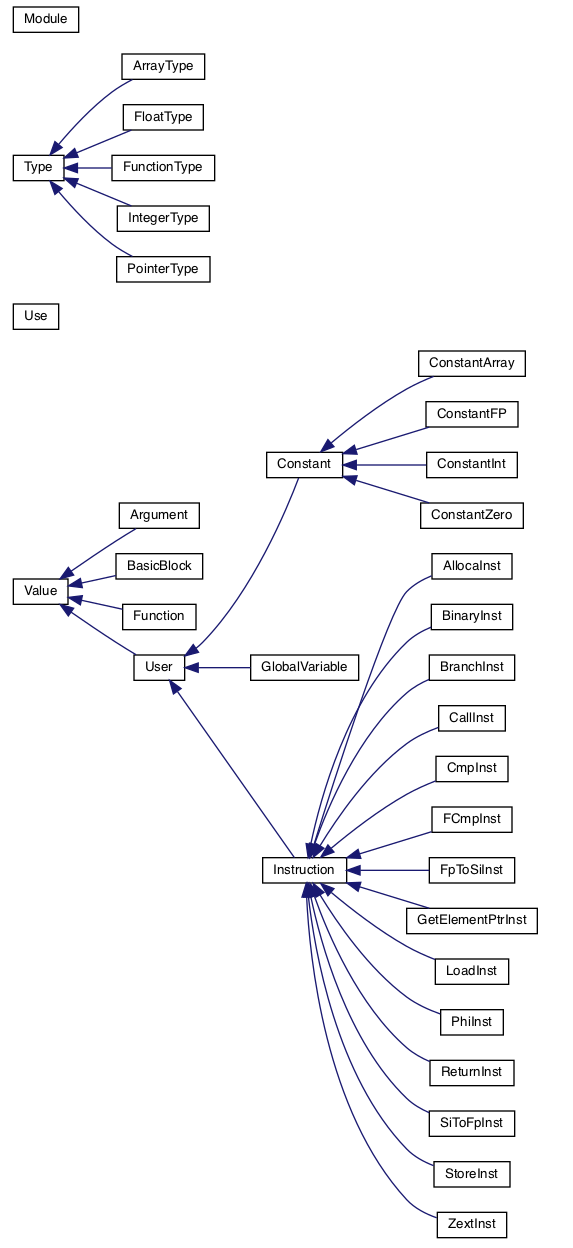
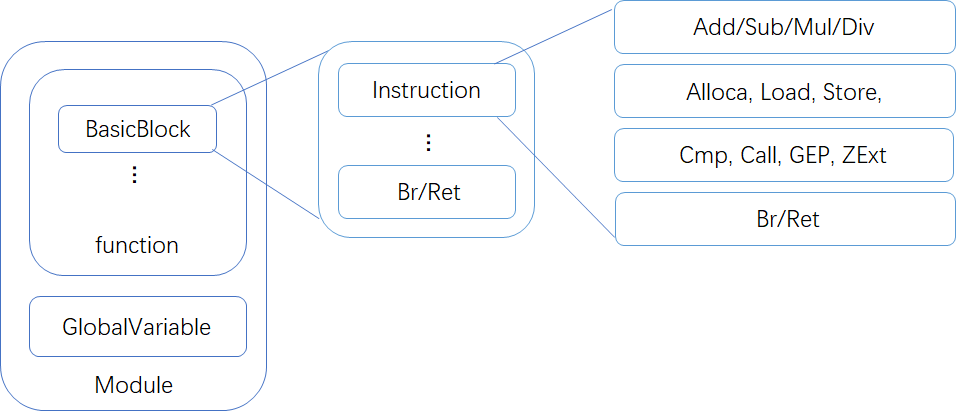
Merge branch 'master' of 202.38.79.174:compiler_staff/2022fall-compiler_cminus
Showing
89.7 KB
32.1 KB
include/lightir/BasicBlock.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/Constant.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/Function.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/IRBuilder.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/IRprinter.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/Module.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/Type.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/User.h
0 → 100644
include/lightir/Value.h
0 → 100644
src/io/CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
src/io/io.c
0 → 100644
src/lightir/BasicBlock.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Constant.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Function.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/IRprinter.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Instruction.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Module.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Type.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/User.cpp
0 → 100644
src/lightir/Value.cpp
0 → 100644